Globalization of the HDPE
PIONEERS IN THE PEAD SUBMARINE PIPE FACILITIES IN VENEZUELA AND RECOGNIZED IN LATIN AMERICA
It is a synthetic polymer, thermoplastic member of polyolefins obtained from a reaction known as polymerization of polyethylene made from ethane, a component of natural gas. In high density polyethylene with higher density, lower permeability, due to its non-polar nature, absorbs very little moisture. It is designated as HDPE (High Density Polyethylene) or HDPE (high density polyethylene).
Applications
- Drinking water supply.
- Irrigation systems.
- Conduction of industrial waste, drainage and wastewate.
- In mining and dredging.
- Driving of natural gas and liquefied petroleum gas.
- General chemical processes.
- Electrical and communication conductors, such as electrical and fiber optic cabling.
What are the characteristics of high density polyethylene?
- Virtually unlimited life on the seabed.
- Excellent thermal and chemical resistance.
- Very good impact resistance.
- It is solid, colorless, translucent, almost opaque.
- Very good processability, that is, it can be processed by the shaping methods used for thermoplastics, such as injection and extrusion.
- It is flexible, even at low temperatures.
- It is not corrosive.
- Interior surface always smooth.
- It is more rigid than low density polyethylene.
- It has difficulties to print, paint or paste on it.
- It’s very light.
- Buoyancy at sea.
- Its density is equal to or less than 0.952 g / cm3.
- It is not attacked by acids, resistant to water at 100 ºC and to most ordinary solvents
Why using HDPE in the construction of submarine pipelines?
For its advantages, it is the best alternative for the construction of submerged structures, which surpass other conventional materials such as steel, cast iron, fiber or concrete. The most outstanding benefits of the HDPE are:
- Lower friction load losses.
- Easy to transport
- It is not attacked by corrosion (does not require cathodic protection).
- Prevents the accumulation of sediments and incrustations inside.
- Long useful life (above 60 years).
- Lower costs of procurement and installation.
- Lower maintenance costs.
- Resistant to seismic movements.
- Elasticity and flexibility to adapt to the terrain topography
Underwater Pipe Systems in HDPE / HDPE
FOCUSED ON DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND INSPECTION
ELINSUBCA is a company that offers professional services of Engineering, Procurement and Construction, since 2002, we have focused on the design, construction and inspection of underwater HDPE polyethylene pipes, intended for Emissaries, Waterworks and Aqueduct installations.
Submarine Emissary
This system works using the natural purification capacity of the oceans through three physical-biological mechanisms: Dilution, Dispersion and Bacterial Decay.
What are they for?
This purification system provides great advantages in the management of wastewater, being very efficient, reliable and robust in its operation; of low investment cost in relation to other technologies and free of maintenance when being built with high density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes.
How do they work ?
Submarine issuing system
An SIDES must also contemplate an environmental monitoring program that allows for comparative measurements, between the before and after the start-up of the project, in order to corroborate the correct functioning of the purification system according to the variables and design results This environmental monitoring program represents the guarantee of a system that was designed to work correctly, since even if optimal results are not achieved, the responsible party would be forced to make improvements in the system to achieve the desired results.
why PEAD?
SUBMARINE INTAKE
Los sistemas de toma de agua construidos en Polietileno de Alta densidad (HDPE siglas en inglés) están destinados a la captación de agua desde una fuente natural como: mares, lagos o ríos.
Los sistemas de toma de agua construidos en Polietileno de Alta densidad (HDPE siglas en inglés) están destinados a la captación de agua desde una fuente natural como: mares, lagos o ríos.
What are they USED FOR?
Submarine outfalls have been used with excellent results in different parts of the world for the management of wastewater from cities and coastal towns, by means of which the natural capacity of the ocean is used to purify the pollutant load of municipal effluents..
This purification system provides great advantages in the management of wastewater, being very efficient, reliable and robust in its operation; of low investment cost in relation to other technologies and free of maintenance when being built with high density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes.
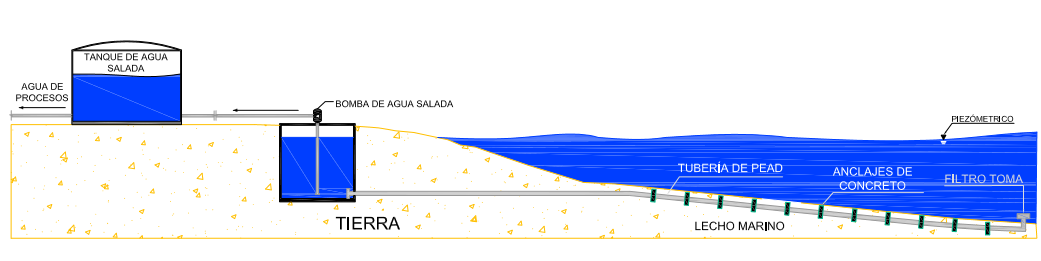
COMMUNICATING VESSEL SYSTEMS ?
A water tap works in a simple way, an example can be seen in the model of “Seawater intake by Communicating Vessel System”. It consists of a pit built on land below sea level, which is connected to the marine environment through an HDPE pipe and a filter that prevents the entry of particularly thick; over the pit of communicating vessels is a pump that sucks salt water to be stored in a tank or to be directly used in the intended application.
For the calculation of the pipeline, the bathymetry studies and marine currents of the area where the system will be installed must be counted; with the purpose of calculating the stability of the pipeline on the seabed and guaranteeing a water quality at the point of capture (low of particles in suspension). The intake pipe is constructed in several long stretches (for example, 300 m long) and reinforced concrete weights, attached to the pipe, are placed to interconnect them in the sea; finally it is necessary the ditching of the pipe in such a way that it remains buried in the seabed, especially in depths less than 10 m.
Specific applications
The applications of the model of “Taking of Sea Water by Communicating Vessel System” are diverse, and can be found mainly in:
Feeding of desalination plants.
Cooling of thermoelectric plants.
Feeding complexes of saltwater pools.
Air conditioning systems cooled by seawater (SWAC acronym in English).
Ocean thermal energy production systems (OTEC acronym in English).
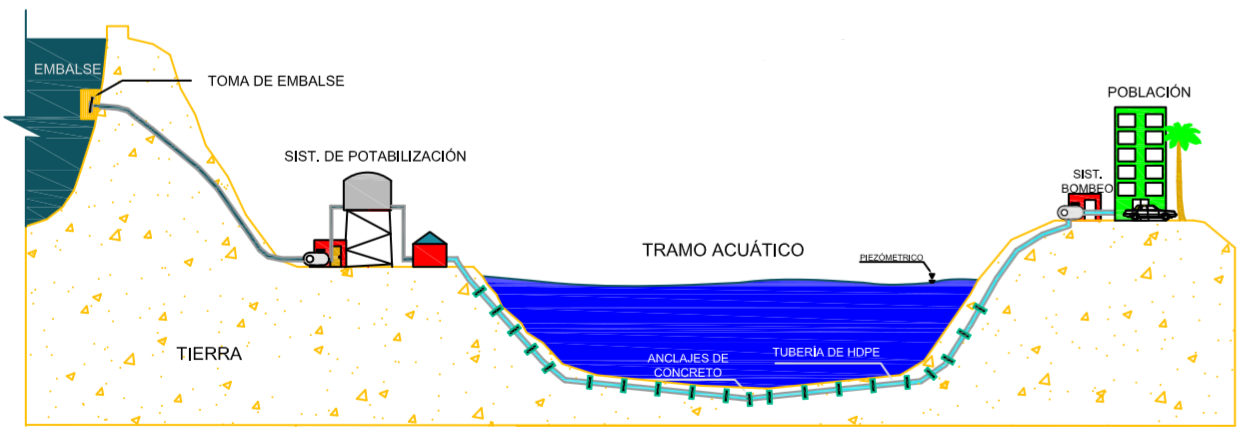
Submarine Aqueduct
Submarine aqueducts are pipelines for the transport of drinking water or raw water through seas, rivers or lakes, in order to serve populations that are isolated by these aquatic environments.
How do they define us?
In the installation of underwater aqueducts, studies must be carried out that determine the most feasible route to bring drinking water service to the towns that require it, from the mainland, normally dams, rivers or lakes, to islands and gulfs. Also, the use of HDPE in subsea aqueducts, consider a wide advantage over traditional materials, reducing maintenance costs, repairs and substitutions.
Examples of underwater aqueducts in operation in Venezuela, currently serving the Margarita and Coche Islands, in the Nueva Esparta state, carrying water from the Turimiquire and Clavellino reservoirs, both located in Sucre State. These aqueducts add more than 120 km of pipe of different diameters (of 200-900 mm) and transport a total of 3200 l / s, to assist a population of approximately 490,000 inhabitants, which can amount to almost 700,000 people in holiday seasons with the influx of vacationers (figures estimated for the year 2012).
How is it built?
The transport is carried out from a reservoir located on the mainland, crossing an aquatic area, which is built with a system of HDPE pipes with reinforced concrete counterweights that are installed in a solidary way along the pipeline. These subsea aqueducts must be constructed by means of long stretches of continuously welded pipes with their flanged ends, of approximate lengths between 300 and 500 m, which are prepared on land and subsequently floated to the installation area to sink them on the seabed.
The long sections are connected to each other by means of flanges, stainless steel fasteners and high pressure gaskets, which allow to ensure the tightness of the system. To ensure adequate protection of the aqueduct, it is necessary to make a submarine ditch to bury the pipeline and leave it out of reach of marine currents and possible collisions with anchors or trawls with fishing nets, especially at depths below 10 m where higher magnitudes of marine currents are reached capable of affecting the stability of the system.
For the design of an underwater aqueduct, current and bathymetry studies should be available to provide detailed information on the variables needed to perform structural calculations and choose the most appropriate route to position the pipeline on the underwater bed. Particularly in submarine aqueducts (unlike submarine outfalls), it is necessary to have shock absorber systems, which are part of the concrete counterweights to limit the forces that may be produced by the expansion of the pipeline as the internal pressure of the system increases.
Long stretches in
large diameters
ELINSUBCA, contributes its experience and knowledge in the installation of High Density Polyethylene Submarine Pipes (HDPE) with the support of the prestigious Pipelife factory in Norway, for the supply of pipes in the Long Stretches in Large Diameters mode, to different projects be developed on the Atlantic coast of Latin American and Caribbean countries.
The manufacture of the pipes, is made in solid wall, up to 2,500 mm diameters, by means of direct continuous extrusion to the ocean, thanks to the strategic location of the Pipelife Norge AS plant by the sea. The sections of pipes are prepared in lengths of up to 550 m, sealing their ends with staggered flanges, to be towed and delivered to their final destination where they will be installed by the contractor.
The towing method is executed directly by the factory, being effective and safe, with more than 50 years of experience executing different projects of great importance around the world. This system provides great advantages in the reduction of time and costs of execution in projects of Emissaries, Submarines and Submarine Aqueducts.